Oral cancer, a silent yet potent threat, affects thousands annually. Understanding this disease is paramount for early detection and successful treatment. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of oral cancer, exploring its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and diverse treatment options. We also illuminate prevention strategies to empower individuals in safeguarding their oral health. By familiarizing yourself with these aspects, you can navigate the landscape of oral cancer with greater awareness and care.
What is Oral Cancer?
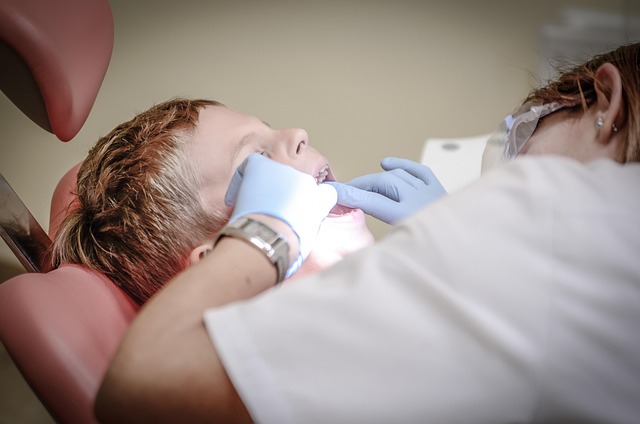
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is a type of cancer that develops in the mouth or the throat. It’s crucial to be aware of this condition due to its significant prevalence globally. The oral cavity includes various parts, such as the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, and hard palate, all of which are susceptible to cancerous growths. These tumors can form on the lining of these tissues, often appearing as abnormal sores or lesions that do not heal.
Early detection is vital in managing oral cancer effectively. Risk factors include tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, sun exposure (for lip cancer), and a history of oral cancer within a family. Recognizing any persistent changes in the mouth, such as red or white patches, lumps, or sore spots, is essential for prompt medical attention. Regular dental check-ups play a significant role in screening and identifying potential oral cancer symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors

Oral cancer, which includes cancers of the mouth, throat, and lips, can arise from various causes and is influenced by several risk factors. The primary drivers include exposure to certain viruses like HPV (human papillomavirus), a history of tobacco use, including smoking and chewing tobacco, and excessive alcohol consumption. These substances can damage the DNA in oral cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and cancer development.
Risk factors for oral cancer extend beyond these causes. Genetic predispositions play a role, with some individuals having a higher genetic likelihood of developing the disease. Additionally, poor oral hygiene and a diet lacking in essential nutrients can contribute. Previous treatment for head or neck cancer, as well as specific environmental exposures like sun exposure (for lip cancer), are also considered risk factors. Understanding these causes and risk elements is crucial for early detection and effective prevention strategies for oral cancer.
Symptoms to Look Out For
Oral cancer symptoms can be subtle or easily overlooked, making it crucial to stay vigilant and regularly examine your mouth. Look for any unusual changes in your oral cavity, including sore spots, ulcers, or red or white patches on the gums, lips, tongue, or throat. These areas may also experience persistent pain, swelling, or bleeding that doesn’t heal within two weeks. Feel for any lumps or thickening of the cheeks, jaw, or neck—signs that could indicate enlarged lymph nodes, a potential indicator of oral cancer.
Don’t dismiss unusual sensations like numbness or difficulty swallowing or speaking. Changes in your voice or persistent bad breath can also be early warning signs. If you notice any persistent symptoms, don’t delay; consult a healthcare professional for a thorough examination and proper diagnosis. Early detection is key to effective treatment outcomes for oral cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options

The diagnosis of oral cancer involves a comprehensive approach, starting with a detailed medical history and physical examination. Dentists or oral surgeons will look for any suspicious lesions, sores, or abnormalities in the mouth, lymph nodes, and surrounding areas. Biopsies are commonly performed to assess the cellular structure of the affected tissue, which helps in confirming the presence and type of oral cancer. Early detection is crucial; regular dental check-ups can significantly improve outcomes.
Treatment options for oral cancer vary based on the stage and location of the tumor. Surgery is often the primary course of action, ranging from simple excision to complex procedures depending on the extent of the cancer. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are also employed to shrink tumors and prevent their spread. Advanced technologies like targeted therapy and immunotherapy offer promising alternatives, particularly for later-stage or recurrent oral cancers. These treatments aim to minimize side effects while maximizing effectiveness.
Prevention Strategies

Prevention is key in combating oral cancer. One of the most effective strategies is regular dental check-ups, allowing for early detection of any unusual growths or lesions. Maintaining good oral hygiene by brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and flossing regularly can significantly reduce the risk. A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides essential nutrients that support overall mouth health. Additionally, limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding tobacco products are crucial, as they are significant risk factors for oral cancer.
Several lifestyle modifications can further prevent oral cancer. This includes protecting your mouth from UV radiation during outdoor activities, wearing a mouthguard during high-impact sports to avoid injuries, and managing stress levels. Reducing or eliminating viral infections like HPV through vaccination is also beneficial, as some studies link these infections to an increased risk of oral cancer.
Oral cancer, while often overlooked, is a serious condition that demands our attention. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early on, and adopting preventive strategies, we can significantly improve outcomes. Remember, regular check-ups and awareness are key to navigating the landscape of oral health. Let’s embrace knowledge as our best defense against this silent threat.
