“Unraveling the mysteries of oral cancer is a vital step towards early detection and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide aims to equip readers with essential knowledge about this often-overlooked form of cancer, affecting the mouth and throat. We delve into the science behind it, from defining the disease to exploring risk factors and symptoms.
Learn about the available treatment options, including surgery, radiotherapy, and innovative targeted therapy. Additionally, discover preventive strategies that can significantly reduce the risk, emphasizing the importance of regular check-ups and lifestyle adjustments.”
What is Oral Cancer? Define and Explain the Type of Cancer Affecting the Mouth and Throat.
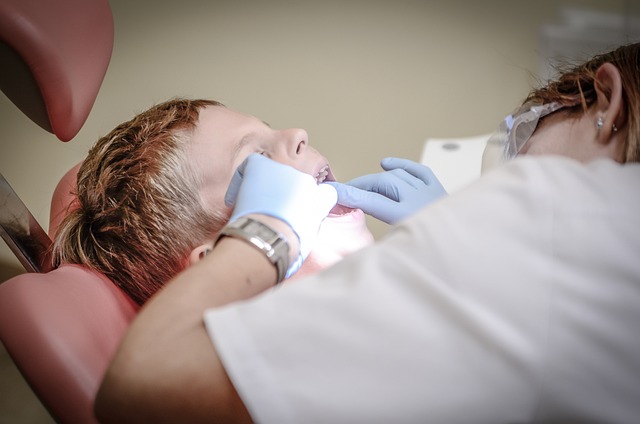
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is a type of cancer that develops in any part of the oral cavity or adjacent structures, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, roof of the mouth, throat, and even the tonsils. It’s important to understand that this cancer can be either malignant (cancerous) or benign (non-cancerous). Malignant oral cancer is a serious condition that requires prompt attention and treatment.
This cancer arises from the cells lining these areas, which can change and grow uncontrollably, forming a tumor. The most common types of oral cancer are squamous cell carcinoma, accounting for around 90% of cases, affecting the thin layer of cells that line the mouth and throat. Another type is adenocarcinoma, which develops in glandular tissue, often in the salivary glands or around the mouth. Early detection is crucial in improving outcomes, so being aware of any unusual changes in the oral cavity or throat is essential for effective management of oral cancer.
Risk Factors: Identify the Potential Causes and Conditions that Can Lead to Oral Cancer Development.
Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, develops when cells in the mouth or throat grow out of control. Understanding the risk factors is a crucial step in preventing and managing this disease. Several potential causes and conditions have been linked to an increased risk of oral cancer. One significant factor is tobacco use, including smoking cigarettes, cigars, or chewing tobacco. These substances contain numerous carcinogens that can damage DNA and lead to cancerous cell growth.
Another critical risk factor is excessive alcohol consumption. Regular and heavy drinking can irritate the mouth’s mucosal tissues, increasing the likelihood of cellular changes that may result in cancer. Additionally, a combination of tobacco and alcohol use compounds the risk significantly. Exposure to certain viruses, such as Human Papillomavirus (HPV), has also been associated with oral cancer development. Poor oral hygiene and previous head or neck radiation therapy are other conditions that can elevate the likelihood of developing this disease.
Symptoms and Detection: Recognize Early Warning Signs, Common Indicators, and Methods for Regular Screening.

Symptoms and Detection: Recognizing Early Warning Signs, Common Indicators, and Methods for Regular Screening
The early detection of oral cancer is crucial for effective treatment. Some common symptoms include unusual lesions or sores in the mouth that do not heal within two weeks, persistent pain or tenderness, changes in the fit of dentures or difficulty swallowing. Other indicators may be red or white patches on the lips, gums, or tongue, and swollen lymph nodes. Any of these signs could be an early warning signal. Regular oral cancer screenings are essential, especially for individuals over 40 years old or those with risk factors such as tobacco use or excessive alcohol consumption.
Methods for screening include visual examinations by healthcare professionals, who look for visible lesions or abnormalities. Additional tools like VELscope, a special light device that enhances the detection of oral abnormalities, and biopsy may be employed if suspicious areas are found. Regular dental check-ups play a vital role in early detection, as dentists can identify potential issues during routine exams. By being aware of these symptoms and undergoing periodic screenings, folks can ensure timely intervention should any signs of oral cancer be present.
Treatment Options: Explore Various Approaches, from Surgery and Radiotherapy to Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy.

When it comes to treating oral cancer, a range of options are available, each with its own advantages and considerations. Surgery is often the first line of defence, involving the removal of the tumour and surrounding tissue. This can range from simple procedures to complex surgeries, depending on the size and location of the cancer.
Beyond surgery, radiotherapy plays a significant role in treating oral cancer by using high-energy beams to shrink tumours and eliminate any remaining cancer cells. Chemotherapy is another common approach, employing drugs to kill rapidly growing cancer cells. More recently, targeted therapy has emerged as an option, focusing on specific molecular changes within cancer cells to halt their growth. These diverse treatment methods allow for a tailored approach to managing oral cancer, catering to individual patient needs and enhancing overall outcomes.
Prevention Strategies: Discuss Lifestyle Changes, Regular Check-ups, and High-Risk Cases to Minimize the Chances of Oral Cancer.

Prevention is key when it comes to oral cancer, and there are several strategies individuals can adopt to minimize their risks. Lifestyle changes play a significant role; adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables, limiting alcohol consumption, and avoiding tobacco products are essential measures. Regular dental check-ups are another crucial component, as dentists can detect early signs of oral cancer during routine examinations.
For those with elevated risk factors, such as a family history of oral cancer or certain genetic mutations, proactive steps are necessary. This may include more frequent dental visits and specialized screenings. Additionally, staying informed about the symptoms of oral cancer—like persistent mouth sores, unusual bleeding, or changes in the lips and gums—enables early detection, which significantly improves treatment outcomes.
Oral cancer, a silent yet potent threat, can be understood and combated through awareness and proactive measures. By recognizing risk factors and early symptoms, such as persistent mouth sores or changes in oral tissues, individuals can facilitate timely detection. Regular dental check-ups play a crucial role in screening for oral cancer, especially for those with elevated risk due to habits like smoking or excessive alcohol consumption. Moreover, adopting preventive strategies, including lifestyle modifications like quitting tobacco use and maintaining a balanced diet, significantly reduces the chances of developing this disease. Armed with knowledge and vigilance, we can navigate the landscape of oral cancer, ensuring better outcomes and quality of life for those affected.
