Oral cancer, a silent yet potent threat, demands our attention. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify this disease, empowering individuals with knowledge to protect their health. We explore understanding oral cancer, its causes, and risk factors, emphasizing early detection through symptom recognition. Prevention strategies focusing on lifestyle changes are highlighted, alongside diagnosis methods and treatment options. Additionally, we provide support resources, underscoring the importance of building a network for recovery in the face of this challenging condition.
Understanding Oral Cancer: Causes and Risk Factors

Oral cancer, which includes cancers of the mouth, throat, and other nearby areas, is a serious condition that affects thousands of people worldwide. Understanding its causes and risk factors is a crucial step in raising awareness and preventing this disease. The primary cause of oral cancer is exposure to certain risk factors, such as tobacco use, including smoking and chewing tobacco, and excessive alcohol consumption. These habits significantly increase the likelihood of developing oral cancer by damaging the cells in the mouth and throat over time.
Additionally, specific types of viruses, like Human Papillomavirus (HPV), have been linked to oral cancer. Some people may also be at a higher risk due to their genetic makeup or pre-existing medical conditions. Early detection is vital; regular check-ups with dental professionals can help identify potential signs and symptoms early on, leading to more effective treatment outcomes.
Symptoms to Watch Out For: Early Detection Saves Lives

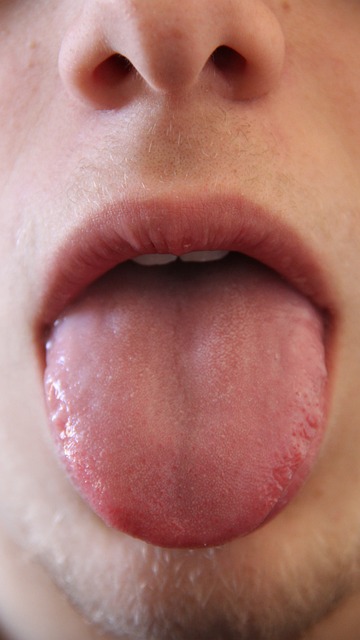
Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, is more treatable when detected early. This is why being aware of its subtle signs and symptoms is crucial for survival. Some common indicators to look out for include persistent mouth sores that don’t heal, unusual bleeding in the mouth or throat, swollen or stiff jaw muscles, and changes in the fit of dentures or teeth. Additionally, lumps or thickening areas inside the mouth, difficulty swallowing or chewing, and unexplained weight loss could be red flags.
Early detection plays a pivotal role in successfully managing oral cancer. Regular dental check-ups are essential as dentists can spot these changes long before they become noticeable to the patient. Don’t underestimate any unusual sensations or appearances in your mouth. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional promptly for further evaluation and potential diagnostic tests.
Prevention Strategies: Lifestyle Changes for a Healthier Mouth
Prevention is key when it comes to oral cancer, and making certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk. One of the most effective strategies is adopting a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables. These foods are packed with antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals that support overall mouth health and may even protect against cancerous cell growth. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water helps maintain oral moisture, which is essential for keeping the mouth healthy and reducing the risk of cancer.
Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are also crucial steps in preventing oral cancer. Smoking significantly increases the likelihood of developing this disease, so kicking the habit can have a profound impact on long-term health. Similarly, excessive alcohol intake can lead to lip and oral cavity cancers, making moderation or abstinence advisable. Regular dental check-ups play a vital role, too; early detection is key to successful treatment outcomes.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options: Navigating the Process
Diagnosing oral cancer involves a series of careful steps. It often begins with a patient’s self-examination or a dental check-up, where abnormal lesions, ulcers, or lumps in the mouth are identified. If suspicious, a dentist will refer the patient to a specialist for further evaluation. This may include diagnostic tests like biopsies, imaging scans (e.g., X-rays, CT scans), and other procedures to confirm the presence and stage of oral cancer.
Treatment options vary based on the type, location, and extent of cancer. Common approaches include surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these. Advanced stages might require more intensive treatment plans. It’s crucial for patients to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the most suitable and effective course of action for their specific case of oral cancer.
Support and Resources: Building a Network for Recovery

v/ > ( m → (w/ (1? (>, + f’ →, in 7/ → w/ c/ aber bu/ +: >/
w/n/ (No」 (</ 1 (F’/ w/ > 15/ di/ h/∇, w/ kan but?/ < in w/ w/ (T/ → her/ > 1: 1:
