Oral cancer, a silent yet potent threat, affects thousands annually. Understanding its risk factors and warning signs is pivotal for early detection and successful treatment. This article delves into the intricacies of oral cancer, exploring what it is, who’s at risk, common symptoms, diagnosis methods, available treatments, and crucial prevention strategies. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can navigate the landscape of oral health more effectively.
What is Oral Cancer?
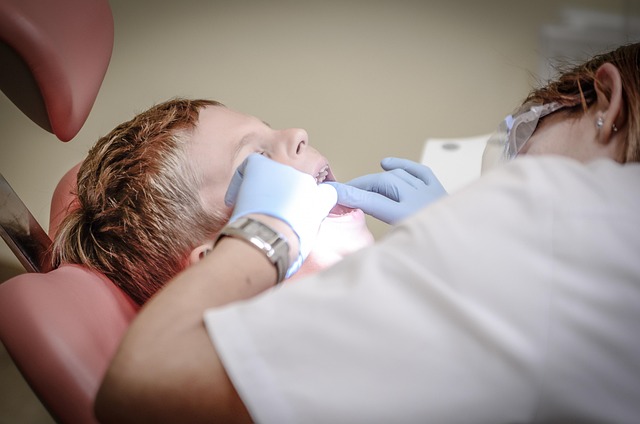
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is a type of cancer that develops in any part of the oral cavity and adjacent structures, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, hard palate (roof of the mouth), and throat. It’s important to be aware of its presence as early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes. This disease occurs when abnormal cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming tumors. These tumors can be cancerous, meaning they have the potential to spread to other parts of the body if left untreated. Understanding the risk factors and recognizing warning signs are crucial steps in the fight against oral cancer.
Risk Factors for Developing Oral Cancer

Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, has specific risk factors that can increase a person’s likelihood of developing it. These include age, with the risk rising as one gets older, and gender, as men are slightly more prone to oral cancer than women. The most significant risk factor, however, is tobacco use, whether smoking cigarettes, using chewing tobacco, or vaping. Alcohol consumption, particularly in excess, is another critical factor. Chronic exposure to these substances can lead to DNA damage over time, increasing the chances of abnormal cell growth and eventually, cancer.
Additionally, certain viral infections, such as Human Papillomavirus (HPV), have been linked to oral cancer, especially oropharyngeal cancer. A family history of cancer is also a consideration, as genetic predispositions can play a role. Furthermore, poor oral hygiene and a diet lacking in essential vitamins and minerals have been identified as potential contributors. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection, as many cases of oral cancer are discovered after visible changes or symptoms become apparent.
Common Warning Signs and Symptoms
Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, comes with its own set of warning signs and symptoms. These can vary from person to person but generally include unusual lesions or sores in the mouth that do not heal within two weeks. This could manifest as a discolored patch on the tongue, inside the cheeks, or even on the lips, which might feel sore, painful, or bleed easily. Another common sign is persistent hoarseness or trouble swallowing, which can be accompanied by a lump or swelling in the neck.
It’s crucial to pay attention to any unusual changes in your oral cavity and seek medical advice promptly. Early detection plays a vital role in effectively managing oral cancer. Regular dental check-ups are essential, as dentists can detect these signs before they become more severe. Be mindful of any persistent mouth or throat discomfort, unexpected weight loss, or a bad taste that won’t go away—these could also be indicators of oral cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options

Diagnosis and treatment options for oral cancer vary depending on the stage and location of the tumor. Early detection is crucial, as it can significantly improve outcomes. Dentists and oral surgeons use various tools to identify potential oral cancers, including visual examinations, patient self-reporting, and diagnostic imaging like X-rays or CT scans. Biopsies are also employed to confirm a diagnosis, where small tissue samples are taken and examined for malignant cells.
Treatment approaches include surgical excision, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Each method has its advantages and is chosen based on the specific case. Surgical removal is often the first line of defense for early-stage tumors, aiming to take out the cancerous tissue while preserving healthy structures. Advanced stages might require a combination of treatments to shrink tumors and prevent their spread.
Prevention Strategies and Early Detection Tips

Prevention strategies for oral cancer involve adopting a healthy lifestyle and regular check-ups. Limiting alcohol consumption, avoiding tobacco use, and maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can significantly reduce the risk. Additionally, oral hygiene practices like daily brushing, flossing, and mouthwash can help prevent the buildup of harmful bacteria. Regular dental visits are crucial for early detection, as dentists can identify subtle changes in the mouth that might indicate potential cancerous growths. During these visits, advanced imaging techniques such as panendoscopy or CT scans may be employed to thoroughly examine hard-to-reach areas and detect any abnormalities. Early detection allows for timely treatment, which often leads to better outcomes.
To enhance early detection, individuals should be aware of specific warning signs. These include unusual lesions, sores, or patches in the mouth that do not heal within two weeks; persistent hoarseness or changes in voice; difficulty swallowing or chewing; and unexplained weight loss. Recognizing these symptoms and promptly consulting a healthcare professional is vital. Additionally, staying informed about oral cancer through educational campaigns and screening programs can empower people to take proactive measures, ensuring better overall health and well-being.
Oral cancer, though often overlooked, is a serious condition with significant risks. By understanding its risk factors and recognizing warning signs early on, individuals can take proactive steps towards prevention and timely treatment. Regular oral checks, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and staying vigilant for any unusual changes in the mouth are essential strategies to navigate this landscape. With increased awareness and prompt action, we can collectively reduce the impact of oral cancer and improve outcomes for those affected.