Oral cancer, a potentially life-threatening condition, affects millions globally. Understanding its nuances is crucial for early detection and effective management. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of oral cancer, covering its definition and various types, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, prevention strategies, and available support. By familiarizing yourself with these aspects, you’ll be better equipped to navigate and combat this disease.
Understanding Oral Cancer: Definition and Types
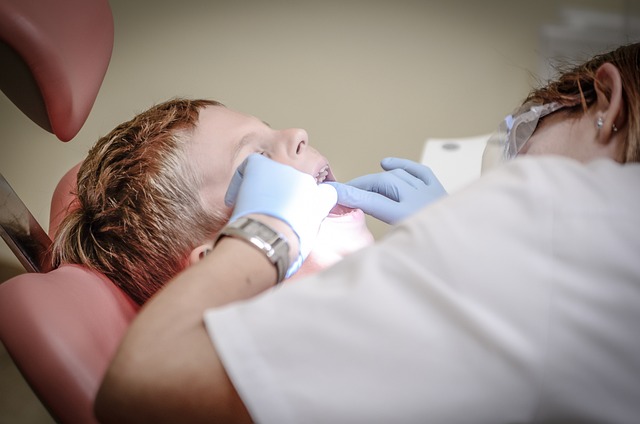
Oral cancer, a term that encompasses cancers forming in the mouth and throat, is a significant health concern worldwide. It’s essential to understand that this disease doesn’t just affect older individuals; younger folks aren’t immune either. The two main types are squamous cell carcinoma, which arises from the thin cells lining the mouth and throat, and adenocarcinoma, developing in glandular tissue. Each type has its own unique characteristics and treatment considerations, emphasizing the need for early detection through regular check-ups.
Recognizing the various symptoms is crucial. These include persistent sores or ulcers in the mouth, unusual bleeding, changes in vocal patterns, and swelling or lumps in the jaw or neck. Timely diagnosis can significantly improve treatment outcomes. By being vigilant and seeking professional advice at the first sign of concern, individuals can navigate the path to better oral health and well-being.
Risk Factors and Common Causes
Oral cancer, a serious condition affecting the mouth and throat, has various risk factors that contribute to its development. Age is a significant factor; the risk increases as individuals get older, with most cases diagnosed in people over 40. Gender also plays a role, as men are statistically more prone to oral cancer than women. Additionally, certain lifestyle choices can elevate the risk. Smoking and chewing tobacco products are well-known causes, significantly increasing the likelihood of oral cancer. Excessive alcohol consumption is another factor, as it irritates the mouth’s delicate tissues.
Genetics also contribute to oral cancer risks. Individuals with a family history of oral or throat cancer may be more susceptible. Moreover, certain medical conditions like human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and a weakened immune system can increase the chances of developing this disease. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun is another less common but still significant cause, particularly for lip cancer. Understanding these risk factors is crucial in early detection and prevention strategies for oral cancer.
Symptoms to Watch For

Oral cancer can be challenging to detect, often presenting subtle symptoms that may go unnoticed. Keep an eye out for any unusual changes in your mouth or throat area. One of the most common signs is a persistent sore or ulcer that doesn’t heal after two weeks. This could be a painless or painful lump, a red or white patch inside the mouth, or a swelling of the jaw or glands.
Don’t ignore any odd sensations, such as numbness or tingling in your teeth or gums, difficulty swallowing or chewing, or persistent hoarseness. In terms of oral cancer, early detection is key, so if you notice any of these symptoms and they persist for more than two weeks, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options

Diagnosis for oral cancer typically begins with a comprehensive oral examination by a dentist or oral surgeon, who will look for any unusual lesions, sores, or discolored patches in and around the mouth. If an abnormality is suspected, further evaluation using specialized tools and imaging techniques may be necessary. Biopsies are commonly performed to obtain a definitive diagnosis, where a small sample of tissue is taken for laboratory analysis.
Treatment options for oral cancer vary depending on the stage and location of the tumor. They may include surgical excision, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these approaches. Early-stage oral cancers often respond well to surgery, while more advanced cases might require a multimodal treatment approach to achieve optimal outcomes. Advances in medical technology have improved survival rates and quality of life for patients diagnosed with oral cancer.
Prevention Strategies and Support Available

Prevention is key when it comes to oral cancer, and there are several strategies individuals can adopt to reduce their risk. Regular dental check-ups are essential; early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Dentists can identify potential risks and provide guidance on lifestyle changes. A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables is recommended, as these foods contain essential nutrients that support overall oral health. Additionally, limiting alcohol consumption and avoiding tobacco products or reducing their use are critical preventive measures, as these habits are strongly linked to a higher risk of developing oral cancer.
Support systems play a vital role in managing the disease. Many organizations offer resources and assistance for patients and their families. These include support groups where individuals can share experiences and gain insights from others facing similar challenges. Online communities and hotlines provide accessible platforms for seeking advice and emotional backing. Furthermore, healthcare professionals can offer counseling and help connect patients to relevant services, ensuring they receive comprehensive care throughout their journey.
Oral cancer, though often overlooked, is a serious condition that requires awareness and proactive measures. By understanding its various aspects, from risk factors to prevention strategies, individuals can take control of their oral health. Regular check-ups, recognizing symptoms early on, and adopting healthy habits are key to minimizing the chances of developing this disease. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to oral cancer, enabling us to make informed decisions for better overall health.
