Oral cancer, a silent yet potent threat, affects thousands annually. Recognizing its subtle signs is crucial for early detection, as timely intervention significantly improves outcomes. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of oral cancer, exploring common symptoms like unusual lesions and persistent pain. We discuss risk factors, diagnosis, treatment options, and emphasize the life-saving power of awareness. Understanding these aspects can empower you to identify potential risks and take proactive measures.
Understanding Oral Cancer: A Comprehensive Overview
Oral cancer, a term that encompasses cancers forming in the mouth, lips, throat, and salivary glands, is a significant health concern worldwide. It’s crucial to recognize that early detection plays a pivotal role in improving treatment outcomes. Understanding the subtle signs and symptoms can empower individuals to seek timely medical advice. This proactive approach is essential, as oral cancer, if left undiagnosed, can lead to severe complications and even be life-threatening.
The causes of oral cancer are diverse, including prolonged exposure to UV radiation, tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain viral infections. Recognizing the early indicators is key. These may include unusual lesions or sores in the mouth that don’t heal, persistent hoarseness, swollen lymph nodes, or a lump or thickening in the mouth or throat. Any changes in oral health warrant attention, as these symptoms could be indicative of various conditions, including pre-cancerous lesions or full-blown cancer.
Common Signs and Symptoms to Watch Out For

Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, exhibits a range of signs and symptoms that can be indicative of an underlying issue. It’s crucial to stay vigilant and watch for any unusual changes in your mouth and throat areas. Common oral cancer symptoms include persistent sores or ulcers in the mouth that do not heal after two weeks; red or white patches on the gums, tongue, or lips; and unexpected bleeding in the mouth, often without any apparent cause.
Other telltale signs can be lumpiness or thickening of the cheek, jaw, or neck; difficulty swallowing or chewing; persistent hoarseness or changes in voice; and a sore throat that does not resolve. If you experience any of these symptoms for more than two weeks, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional as they could be indicative of oral cancer, which is highly treatable when detected early.
Risk Factors and Potential Causes
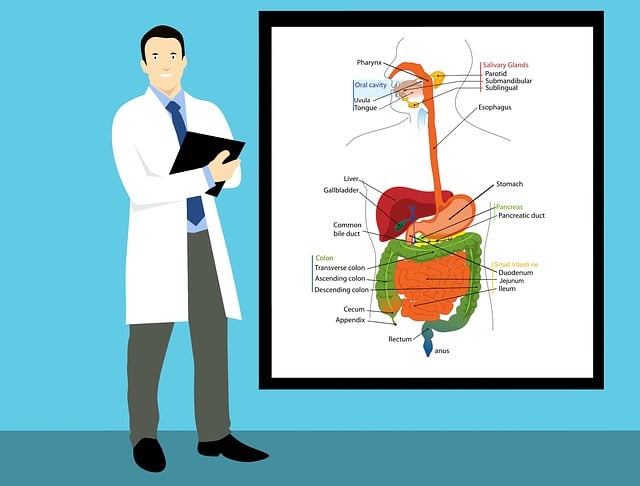
Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, has various risk factors and potential causes. Some of the primary risks include prolonged exposure to UV radiation, which can affect the lips; tobacco use, both smoking and chewing, significantly increases the chances of developing oral cancer; excessive alcohol consumption is another well-documented cause; and a history of previous oral cancer or chronic lip or mouth sores.
Genetics also play a role, as certain inherited conditions and gene mutations can predispose an individual to oral cancer. Additionally, poor oral hygiene and a weak immune system can contribute to the development of this disease. It’s essential to be aware that many cases of oral cancer have no apparent cause, highlighting the complex interplay between various factors in the development of this condition.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options

Diagnosis for oral cancer typically begins with a comprehensive oral examination and medical history review by a dentist or oral surgeon. They will look for any unusual lesions, sores, or discolored patches in the mouth that may persist for more than two weeks. If an abnormality is detected, further diagnostic procedures such as biopsy, imaging tests (including X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs), and tissue samples analysis might be recommended. Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes for oral cancer.
Treatment options for oral cancer vary based on the stage and location of the tumor. They may include surgical excision to remove the cancerous tissue, radiation therapy to shrink tumors and kill any remaining cancer cells, chemotherapy to destroy cancer cells, or a combination of these approaches. In some cases, targeted therapy or immunotherapy might be used to specifically target the unique characteristics of oral cancer cells. Reconstructive surgery can also be necessary to restore mouth function and appearance after treatment.
Early Detection: Saving Lives Through Awareness
Early detection plays a pivotal role in saving lives and improving outcomes for those affected by oral cancer. By being aware of the subtle changes in your mouth and regularly examining yourself, you can significantly enhance your chances of identifying oral cancer at its earliest stages. This proactive approach allows for timely treatment, which often leads to better results.
Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, is more treatable when caught early. Common signs to look out for include unusual lesions or moles in the mouth, persistent sore throats, changes in the fit of dentures, and new or altered sensations (numbness or tingling) in the oral area. Regular dental check-ups are essential as dentists can detect these subtle changes and guide you towards appropriate further evaluation. Stay vigilant, and don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if any concerning symptoms persist for more than two weeks.
Oral cancer, though less discussed, is a serious health concern that requires heightened awareness. By recognizing the common signs and symptoms, understanding risk factors, and staying informed about diagnosis and treatment options, individuals can significantly improve their chances of early detection. Early intervention is key to saving lives, making it crucial for everyone to stay vigilant and prioritize oral health. Regular check-ups and a proactive approach towards any unusual changes in the mouth can make all the difference in the fight against oral cancer.
