Oral cancer, a silent yet potent threat, affects thousands annually. Understanding its subtle signs and symptoms can mean the difference between life and death. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of oral cancer, exploring causes, risk factors, early detection methods, diagnosis, treatment, recovery, and prevention strategies. By familiarizing yourself with these aspects, you’ll be better equipped to protect your oral health and catch any potential issues early on.
Understanding Oral Cancer: Causes and Risk Factors

Oral cancer, a serious condition affecting the mouth and surrounding areas, is crucial to understand given its rising prevalence. Caused by abnormalities in cells lining the oral cavity, it can originate in various parts including the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, or gum tissue. Several risk factors contribute to its development, making awareness and early detection vital.
The primary risk factors include tobacco use, both smoking and chewing, which significantly increases the likelihood of oral cancer. Excessive alcohol consumption is another notable contributor. Additionally, certain viral infections like Human Papillomavirus (HPV) have been linked to a higher incidence of oral cancer. Age is also a factor, with the risk rising as individuals get older. Furthermore, genetic predispositions and a history of prior oral cancer play significant roles in determining an individual’s susceptibility.
Symptoms to Watch for: Early Detection is Key

Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, is easier to treat and manage when detected early. It’s crucial to be aware of the subtle signs and symptoms that may indicate a potential issue. Watch for unusual changes in your mouth, such as persistent sores or lesions that don’t heal within two weeks. These could be red, white, or ultra-red patches on the gums, tongue, or lips. Any new or altered moles or bumps inside the mouth are also worth noting.
Additionally, feel for any thickening or lump formation in the oral cavity, jaw, or neck. Changes in bite patterns and persistent hoarseness or difficulty swallowing can be indicators as well. Regular dental check-ups play a vital role in early detection. Don’t hesitate to consult your dentist if you notice any of these symptoms, as timely action could make all the difference in managing oral cancer effectively.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options Explained
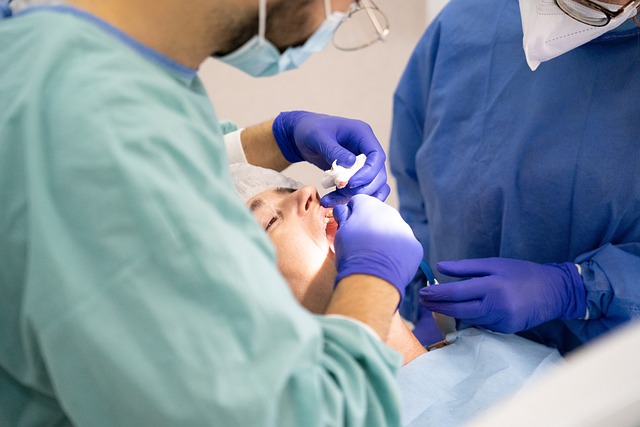
Diagnosis for oral cancer typically begins with a comprehensive oral examination and medical history review by a dentist or oral surgeon. If an abnormality is suspected, further diagnostic procedures such as biopsy, where a small tissue sample is taken for analysis, are conducted. This process helps to determine the type and extent of the cancer, crucial in tailoring effective treatment plans.
Treatment options for oral cancer vary based on the stage and location of the tumor. They include surgical excision, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Each approach has its advantages and potential side effects. Surgical removal is common for early-stage tumors, while advanced cases might require a combination of treatments to enhance survival rates and quality of life post-therapy.
Recovery Process and Long-Term Management

The recovery process for oral cancer varies greatly depending on the stage and location of the tumor. Early-stage cancers often respond well to treatment, with surgical excision being a common approach. This is followed by radiation therapy or chemotherapy to ensure all remaining cancer cells are eradicated. Patients may experience side effects during and after treatment, such as pain, swelling, and changes in taste or chewing abilities, but these usually subside over time.
Long-term management involves regular check-ups and screenings to monitor for recurrence. Rehabilitation may include speech therapy, physical therapy, or dental work to restore oral functionality and comfort. Support groups can also be beneficial, connecting patients with others who have faced similar challenges, providing emotional support and practical advice for living with and managing oral cancer.
Prevention Strategies: Protecting Your Oral Health
Preventing oral cancer is a proactive approach to maintaining optimal oral health. Key strategies include adopting a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet, avoiding tobacco products, and moderating alcohol consumption. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection, as they allow dentists to identify potential risks or anomalies.
Furthermore, staying informed about oral cancer risk factors, such as genetics and certain viral infections, empowers individuals to make informed decisions. Using sun protection for lips, practicing good oral hygiene, and avoiding excessive sugar intake also contribute to a comprehensive prevention plan, helping to reduce the likelihood of developing this disease.
Oral cancer, though often overlooked, is a serious health concern. By understanding its causes, recognizing early symptoms, and adopting preventive strategies, individuals can significantly improve their oral health outcomes. Early detection through regular check-ups and awareness of potential risks can lead to successful treatment and recovery. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to protecting your mouth and overall well-being from the effects of oral cancer.
