“Oral cancer, a silent yet serious health concern, affects thousands worldwide. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify every aspect of this disease. From understanding its defining characteristics to exploring risk factors, symptoms, and available treatments, we provide an insightful overview. Learn about the latest diagnosis techniques and effective prevention strategies. Discover how early detection can significantly impact outcomes. By familiarizing yourself with oral cancer, you gain valuable knowledge for maintaining optimal oral health.”
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is a type of cancer that develops in any part of the oral cavity or nearby areas, including the lips, tongue, cheeks, floor of the mouth, throat, and even the glands that produce saliva. It’s important to understand that early detection plays a crucial role in successful treatment outcomes for oral cancer. This is because symptoms often develop gradually and may be mistaken for other less serious conditions.
Risk factors for oral cancer include tobacco use (smoking or chewing), excessive alcohol consumption, sun exposure (particularly to the lips), poor oral hygiene, and a history of head or neck cancer. However, it’s worth noting that anyone can develop oral cancer, regardless of their lifestyle choices or age. Recognizing the signs and symptoms, such as persistent mouth sores, lumps or thickening in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, or changes in bite, is essential for timely medical intervention.
Causes and Risk Factors

Oral cancer, which includes cancers of the mouth, throat, and related structures, is caused by abnormal cell growth that can be influenced by various factors. The primary driver is usually exposure to certain risk factors. These include excessive alcohol consumption, use of tobacco products, and prolonged sun exposure for lip cancer. Poor dietary habits, specifically a diet low in fruits and vegetables, are also linked to an increased risk. Additionally, genetic predisposition plays a role, with some individuals having a higher likelihood due to inherited genes. Viral infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV), have been identified as contributors, especially for oropharyngeal cancer. Furthermore, certain environmental factors like chewing betel nut and exposure to specific chemicals can elevate the risk of developing oral cancer.
Symptoms to Look Out For
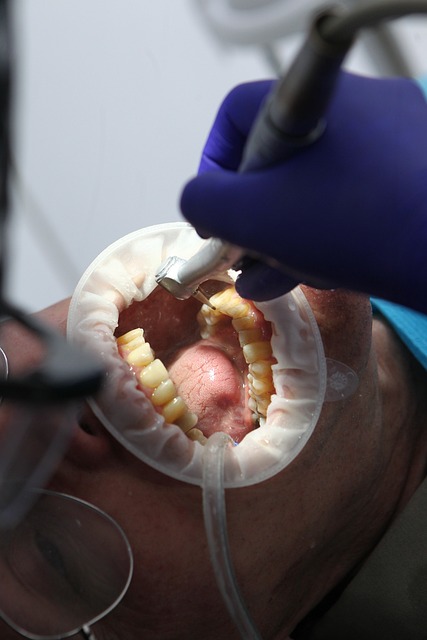
Oral cancer symptoms can often be subtle and easily overlooked, which is why regular dental check-ups are crucial. Look out for any unusual changes in your mouth, such as persistent sores or ulcers that don’t heal within two weeks, red or white patches on the gums, tongue, or lips, or a lump or thickening of oral tissues. Additionally, watch for difficulty swallowing, persistent hoarseness, or unexplained weight loss. Early detection is key to successful treatment, so any unusual symptoms should be promptly evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Don’t ignore changes in your bite or fit of dentures, as these could indicate swelling or movement of oral structures. Pain or tenderness in the jaw, face, or neck that persists without an obvious cause is another red flag. In some cases, patients may notice a change in their voice or breathing, especially if cancer has spread to nearby areas. Being aware of these potential signs can help ensure timely diagnosis and treatment for oral cancer.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options

Diagnosis for oral cancer typically involves a comprehensive approach, starting with a detailed medical history and physical examination by a dental professional or oncologist. They will look for any abnormal lesions, ulcers, or discolored patches in the mouth, tongue, gums, lips, or throat. Biopsies may be performed to take tissue samples for microscopic analysis, which is crucial for an accurate diagnosis. This process allows healthcare providers to determine if cancer cells are present and, if so, their type and stage.
Treatment options for oral cancer vary based on the stage and location of the tumor. Standard treatments include surgery to remove the cancerous tissue, radiation therapy to shrink tumors, and chemotherapy to destroy any remaining cancer cells. Advanced technologies like laser surgeries and targeted drug therapies are also employed to enhance precision and minimize side effects. Additionally, support services such as speech therapy and counseling can significantly aid patients in their recovery journey.
Prevention Strategies and Prognosis

Prevention is key in combating oral cancer, as early detection can significantly improve outcomes. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for maintaining overall oral health and identifying potential risks. Dentists can examine areas that are often missed by self-inspection, including the tongue, gums, and mouth lining. Simple lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, and adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables can significantly reduce the chances of developing oral cancer.
Prognosis for oral cancer varies based on several factors, including the stage at diagnosis and the location of the tumor. Early-stage cancers often have better outcomes, with treatment options ranging from surgical excision to radiation therapy. Advanced stages may require a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. Proactive monitoring and understanding these prevention strategies can empower individuals to take control of their oral health and potentially avoid this serious disease.
Oral cancer, though often overlooked, is a serious condition that demands our attention. By understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms, and adopting preventive measures, we can significantly improve outcomes. Early detection through regular check-ups and awareness of risk factors is key to effective treatment. With the right strategies in place, oral cancer’s prognosis can be favorable, emphasizing the importance of staying informed and proactive regarding this health issue.
